Although one of the least explored senses in the field of research, the sense of smell (or olfaction) may be one of the most important senses for overall health. Smell has a unique relationship with memory and emotions that is unmatched. No doubt you’ve experienced déjà vu due to exposure to a scent. This familiar and memorable aroma—like grandma’s oatmeal chocolate chip cookies, your dad’s garage, new car smell, or the flowers outside the house you grew up in—activates specific areas of your brain reigniting vivid memories and emotions. These nostalgic experiences intimately linked to aromas are called scent memories and demonstrate just how powerful the sense of smell is.
Your sense of smell is directly connected to your brain. Functional magnetic resonance imaging shows that when you smell something two parts of the brain are activated—the amygdala and hippocampus. The amygdala is the emotional center of the brain and the hippocampus plays a major role in memory, so it is not surprising that scents arouse powerful memories and emotions. Indeed, a captivating and familiar aroma has the power to not only remind you of a past person, place, or event, but it triggers emotions more powerful than those generated by other senses like sight and sound. (1)
Collectively, the amygdala and hippocampus (both parts of your limbic system) coordinate a conditioned response that rapidly links familiar aromas with their associated memories. Other senses (visual, auditory, and tactile) do not pass through these areas of the brain, which explains why aromas produce greater emotional responses than the other senses.
 Scientists are just beginning to understand the complexity of the sense of smell and its involvement in human health. The discovery of olfactory receptors outside the nasal cavity in areas such as the kidneys, heart, skin, and immune cells highlighted a wider role for olfaction in human health than previously known. (2) A growing body of evidence suggests that olfactory receptors not only play a role in the function of multiple organs and systems, but they also have potential to be used in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of disease. (3) This research has revealed that olfactory receptors perform important functions such as:
Scientists are just beginning to understand the complexity of the sense of smell and its involvement in human health. The discovery of olfactory receptors outside the nasal cavity in areas such as the kidneys, heart, skin, and immune cells highlighted a wider role for olfaction in human health than previously known. (2) A growing body of evidence suggests that olfactory receptors not only play a role in the function of multiple organs and systems, but they also have potential to be used in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of disease. (3) This research has revealed that olfactory receptors perform important functions such as:
- Regulate heart function.
- Promote death and reduce the spread of certain types of cancer cells.
- Regenerate skin cells to speed the wound healing process.
- Promote prostate health.
- Aid digestion.
- Regulate blood pressure.
- Stimulate insulin secretion by the pancreas. (4)
- Regulate appetite. (5)
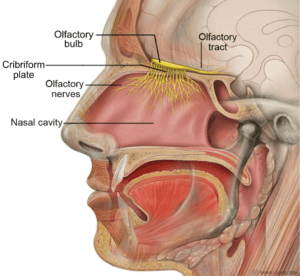 Nostalgic memories and positive emotions can also be produced by the potent aromatic molecules found within essential oils. When an essential oil is smelled, aromatic molecules are carried by olfactory sensory neurons to the olfactory bulb. The olfactory bulb filters and processes the incoming signals and then mitral cells carry an outgoing signal to the olfactory cortex and the limbic system, which includes the amygdala and the hippocampus. A wide variety of psychophysiological responses occur in response to this outgoing signal that can promote improved health. Here are a few essential oils associated with improved memory and emotions:
Nostalgic memories and positive emotions can also be produced by the potent aromatic molecules found within essential oils. When an essential oil is smelled, aromatic molecules are carried by olfactory sensory neurons to the olfactory bulb. The olfactory bulb filters and processes the incoming signals and then mitral cells carry an outgoing signal to the olfactory cortex and the limbic system, which includes the amygdala and the hippocampus. A wide variety of psychophysiological responses occur in response to this outgoing signal that can promote improved health. Here are a few essential oils associated with improved memory and emotions:
- Citrus oils like lemon, orange, and tangerine are strongly uplifting. Inhalation of citrus fragrance helped normalize neuroendocrine hormone levels and immune function in people diagnosed with depression and was deemed more effective than antidepressants. (6)
- Rosemary is called the herb of remembrance and for good reason. Teen boys and girls (aged 13 to 15 years old) experienced significantly improved short-term memory when they inhaled rosemary essential oil. (7)
- Lavender essential oil is associated with a more relaxed state. Healthy individuals who inhaled lavender essential oil reported feeling fresher and more relaxed than individuals who inhaled a base oil. (8)
These few studies—and many more existing studies—show that essential oils can improve mood and memory function simply through inhalation. For more research to support the use of essential oils for memory and emotions, see Medicinal Essential Oils: The Science and Practice of Evidence-based Essential Oil Therapy.
The power of the sense of smell should not be overlooked nor underestimated. The evidence is clear that olfaction plays a significant role in overall human health, so don’t cut your health short. Stop to smell the roses and be sure to incorporate essential oil inhalation into your regular daily routine.
Great article. Thanks for sharing it and all the other information you send out daily.
Comments are closed.